PVC Pipe Sizes
When it comes to plumbing, irrigation, or construction projects, understanding PVC pipe sizes is essential. PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) pipes are among the most widely used materials for piping systems worldwide because they are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, affordable, and long-lasting. However, choosing the right pipe size can be confusing due to various standards and dimensions.
This complete PVC pipe size chart and guide will help you understand the different sizes of PVC pipe, how to read the dimensions, and how to select the right size for your project.

What Is PVC Pipe?
PVC pipe is made from polyvinyl chloride, a durable thermoplastic material used for transporting water, chemicals, and waste. It’s popular in plumbing, agriculture, and industry due to its strength, low cost, and easy installation.
PVC pipes come in multiple types and schedules, which determine their wall thickness and pressure capacity. The most common types include:
- Schedule 40 PVC pipe – standard wall thickness, used for residential plumbing and irrigation.
- Schedule 80 PVC pipe – thicker walls, higher pressure rating, used for industrial and commercial systems.
Understanding the PVC pipe dimensions in mm is crucial to ensure proper fit and function in your project.
Understanding PVC Pipe Size Dimensions
One of the most common misconceptions is that pvc plastic pipe dimensions refer to the inner diameter (ID), but that’s not always true. PVC pipes are classified by their nominal size, which is a standardized measurement and may not match the actual ID or OD.
Here’s what you need to know about PVC plastic pipe sizes:
| Term | Description |
| Nominal Size (NPS) | The standardized pipe size name (e.g., 1″, 2″, 4″). |
| Outer Diameter (OD) | The outside width of the pipe measured edge to edge. |
| Inner Diameter (ID) | The inside width of the pipe (varies by wall thickness). |
| Wall Thickness | The difference between OD and ID. |
| Schedule Number | A code indicating wall thickness (e.g., Schedule 40, 80). |
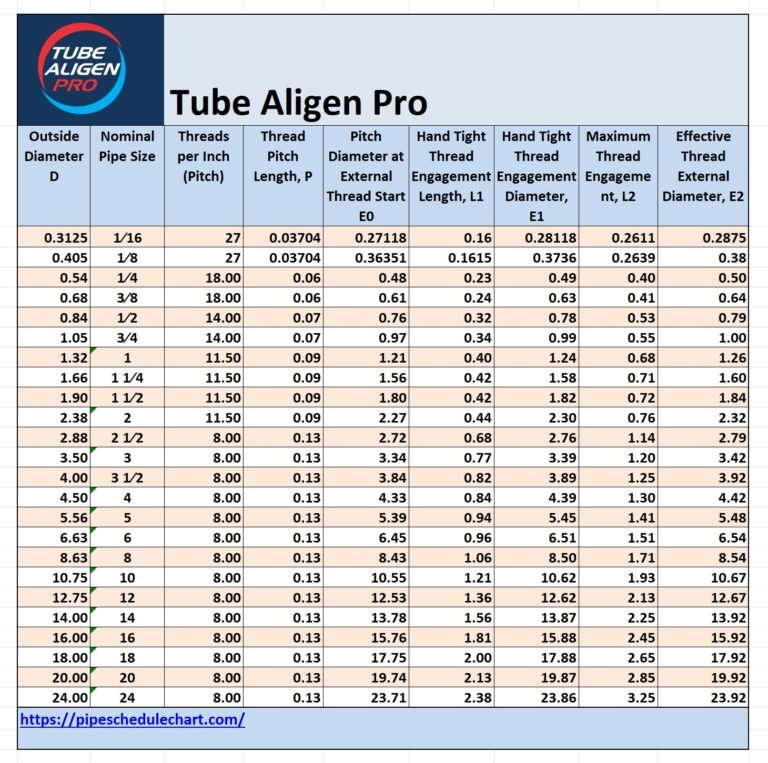
PVC Pipe Size Chart (Inches and Millimeters)
Below is a comprehensive PVC pipe size chart showing the nominal size, outside diameter, inside diameter, and wall thickness for Schedule 40 pipes — the most common standard used in residential and commercial systems.
Schedule 40 PVC Pipe Dimensions (Nominal sizes 1/8″ — 24″)
Table shows nominal pipe size, outside diameter (O.D.), average inside diameter (I.D.), minimum wall thickness, nominal weight per foot and maximum working pressure (PSI).
| Nom. Pipe Size (in) | O.D. | Average I.D. | Min. Wall | Nominal Wt./Ft. | Maximum W.P. PSI* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/8 | 0.405 | 0.249 | 0.068 | 0.051 | 810 |
| 1/4 | 0.540 | 0.344 | 0.088 | 0.086 | 780 |
| 3/8 | 0.675 | 0.473 | 0.091 | 0.115 | 620 |
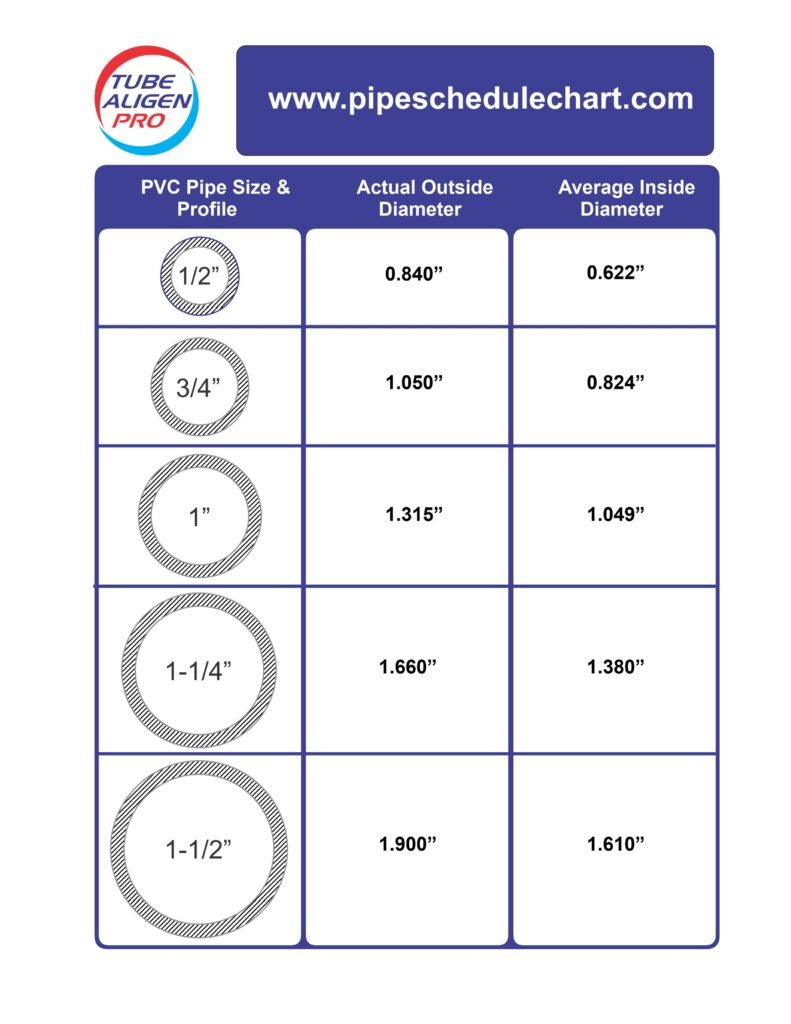
| 1/2 | 0.840 | 0.602 | 0.109 | 0.170 | 600 |
| 3/4 | 1.050 | 0.804 | 0.113 | 0.226 | 480 |
| 1 | 1.315 | 1.029 | 0.133 | 0.333 | 450 |
| 1-1/4 | 1.660 | 1.360 | 0.140 | 0.450 | 370 |
| 1-1/2 | 1.900 | 1.590 | 0.145 | 0.537 | 330 |
| 2 | 2.375 | 2.047 | 0.154 | 0.720 | 280 |
| 2-1/2 | 2.875 | 2.445 | 0.203 | 1.136 | 300 |
| 3 | 3.500 | 3.042 | 0.216 | 1.488 | 260 |
| 3-1/2 | 4.000 | 3.521 | 0.226 | 1.789 | 240 |
| 4 | 4.500 | 3.998 | 0.237 | 2.118 | 220 |
| 5 | 5.563 | 5.016 | 0.258 | 2.874 | 190 |
| 6 | 6.625 | 6.031 | 0.280 | 3.733 | 180 |
| 8 | 8.625 | 7.942 | 0.322 | 5.619 | 160 |
| 10 | 10.750 | 9.976 | 0.365 | 7.966 | 140 |
| 12 | 12.750 | 11.889 | 0.406 | 10.534 | 130 |
| 14 | 14.000 | 13.073 | 0.437 | 12.462 | 130 |
| 16 | 16.000 | 14.940 | 0.500 | 16.286 | 130 |
| 18 | 18.000 | 16.809 | 0.562 | 20.587 | 130 |
| 20 | 20.000 | 18.743 | 0.593 | 24.183 | 120 |
| 24 | 24.000 | 22.544 | 0.687 | 33.652 | 120 |
PVC Pipe Schedule 80
Schedule 80 PVC Pipe Dimensions (1/8″ to 24″)
This table provides nominal pipe size, outside diameter (O.D.), inside diameter (I.D.), minimum wall thickness, nominal weight per foot, and maximum working pressure (PSI) for Schedule 80 PVC pipes.
| Nominal Pipe Size (in) | O.D. (in) | Average I.D. (in) | Min. Wall (in) | Nominal Wt./ft. | Maximum W.P. PSI* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/8 | 0.405 | 0.195 | 0.095 | 0.068 | 1230 |
| 1/4 | 0.540 | 0.282 | 0.119 | 0.115 | 1130 |
| 3/8 | 0.675 | 0.403 | 0.126 | 0.158 | 920 |
| 1/2 | 0.840 | 0.526 | 0.147 | 0.232 | 850 |
| 3/4 | 1.050 | 0.722 | 0.154 | 0.314 | 690 |
| 1 | 1.315 | 0.936 | 0.179 | 0.461 | 630 |
| 1-1/4 | 1.660 | 1.255 | 0.191 | 0.638 | 520 |
| 1-1/2 | 1.900 | 1.476 | 0.200 | 0.773 | 470 |
| 2 | 2.375 | 1.913 | 0.218 | 1.070 | 400 |
| 2-1/2 | 2.875 | 2.290 | 0.276 | 1.632 | 420 |
| 3 | 3.500 | 2.864 | 0.300 | 2.186 | 370 |
| 4 | 4.500 | 3.786 | 0.337 | 3.196 | 320 |
| 6 | 6.625 | 5.709 | 0.432 | 6.102 | 280 |
| 8 | 8.625 | 7.565 | 0.500 | 9.269 | 250 |
| 10 | 10.750 | 9.493 | 0.593 | 13.744 | 230 |
| 12 | 12.750 | 11.294 | 0.687 | 18.909 | 230 |
| 14 | 14.000 | 12.410 | 0.750 | 22.681 | 220 |
| 16 | 16.000 | 14.213 | 0.843 | 29.162 | 220 |
| 18 | 18.000 | 16.014 | 0.937 | 36.487 | 220 |
| 20 | 20.000 | 17.814 | 1.031 | 44.648 | 220 |
| 24 | 24.000 | 21.418 | 1.218 | 63.341 | 210 |
PVC Pipe Size Conversion: Inches to mm
If you’re working on international projects or using mixed measurement systems, these quick conversions will help:
- 1/2 inch = 21.34 mm
- 3/4 inch = 26.67 mm
- 1 inch = 33.40 mm
- 2 inch = 60.33 mm
- 4 inch = 114.30 mm
- 6 inch = 168.28 mm
- 8 inch = 219.08 mm
Pro tip: Always double-check your fittings and connectors — some fittings are sized for metric systems while others follow imperial standards.
How to Read and Measure PVC Pipe Sizes
Measuring PVC pipes isn’t complicated once you know what to look for. Here’s a simple way to do it:
- Find the printed marking on the pipe — it usually lists size, schedule, and pressure rating.
- Measure the Outer Diameter (OD) — use calipers or a measuring tape across the pipe.
- Match the OD to the closest nominal size in a PVC pipe size chart.
- Select fittings that match your nominal pipe size (not the measured diameter).
For example, a 1-inch PVC pipe actually measures 1.315 inches OD, but you’ll still use 1-inch fittings.
What People Use PVC Pipes For by Size
Each size of PVC pipe has a specific purpose based on how much water needs to flow and how it will be used:
Pipe Size and Common Uses
Common PVC Pipe Sizes and Their Uses
Different PVC pipe sizes serve different purposes. Here’s a practical breakdown:
| Pipe Size | Typical Use |
| 1/2″ – 3/4″ | Garden hoses, small water lines, drip irrigation |
| 1″ – 2″ | Home plumbing, water distribution, drainage |
| 3″ – 4″ | Sewage lines, vent systems, main drains |
| 6″ – 8″ | Industrial systems, stormwater lines |
| 10″ – 12″ | Municipal water mains, large-scale irrigation |
Schedule 40 vs. Schedule 80 PVC Pipes
One of the most common questions people ask is, “What’s the difference between Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 pipes?”
It’s simple — the schedule number refers to wall thickness.
| Type | Wall Thickness | Pressure Capacity | Color | Common Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Schedule 40 | Standard | Up to 280 PSI | White | Plumbing, irrigation |
| Schedule 80 | Thicker | Up to 400 PSI | Gray | Industrial, high-pressure systems |
If you’re building a home irrigation line, Schedule 40 is usually enough. But for factory or chemical use, Schedule 80 offers more durability and safety.
How to Choose the Right PVC Pipe Size
Choosing the correct PVC pipe size is about more than just diameter. Here are some professional tips:
- Calculate your flow rate – How much water or fluid will pass through?
- Check the pressure rating – Make sure your pipe can handle it.
- Consider temperature – PVC loses strength at higher temperatures.
- Match the fittings – Always use the same nominal size for all joints.
- Factor in wall thickness – Thicker walls reduce inner diameter, slightly affecting flow.
- Pvc internal diameter -for berrer fitting and flow rate calculations
Getting these details right saves time, money, and future leaks.
Advantages of PVC Pipes
PVC remains a favorite material for both homeowners and professionals because of its many benefits:
- Lightweight and easy to handle
- Doesn’t rust or corrode
- Affordable and readily available
- Lasts for decades with minimal maintenance
- Smooth inner surface for better water flow
- Environmentally friendly (recyclable)
In short, PVC pipes are reliable, long-lasting, and perfect for nearly any type of fluid transfer system.
PVC Pipe Standards and Quality Marks
All PVC plastic pipe sizes are manufactured under strict standards to ensure performance and compatibility. The most common ones include:
- ASTM D1785: Dimensions and pressure ratings for PVC pipes
- ASTM D2466: PVC fittings specifications
- ISO 1452: International metric standard for PVC pressure pipes
- BS EN 1452: British and European standard for water supply PVC pipes
Always check the standard code printed on your pipe to confirm it meets local requirements.
FAQs About PVC Pipe Size Chart
conclusion
Choosing the right PVC pipe size isn’t just about guessing what looks right — it’s about understanding how dimensions, wall thickness, and pressure ratings affect performance.
With this PVC pipe size chart and guide, you now know exactly how to read pipe markings, compare schedules, and convert sizes from inches to millimeters. Whether you’re a DIY homeowner or a professional installer, this knowledge helps ensure leak-free, efficient systems that last for decades.
So next time you’re shopping for pipes, bring this chart along — it’s your quick, reliable tool for choosing the perfect PVC pipe size for any job.