Pipe Schedule Chart
Pipe Chart Schedule
A Comprehensive Guide to Pipe Sizes, Schedules, and Dimensions
At Tube Aligen Pro, Our mission to provide accurate and updated information. The Pipe Schedule Chart is an indispensable tool in industries ranging from plumbing to the oil and gas industry.
It standardizes pipe dimensions, ensuring compatibility, safety, and efficiency. This guide explores the fundamentals of pipe schedules, steel pipe dimensions, and how to interpret chart for optimal project outcomes.

What is Pipe chart schedule

A pipe diameter chart defines the relationship between Nominal Pipe Size (NPS), outer diameter (OD), and wall thickness. This pipe size charts categorize pipes into schedules (e.g., Sch 40, Sch 80) to indicate their pressure-handling capabilities and applications.
There are two Commonly used standers in USA
ANSI (American National Standards Institute)
ANSI is a private nonprofit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, and systems in the United States.
ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers)
ASME is a professional association focused on mechanical engineering and multidisciplinary technical fields.
Key Components of a Piping Schedule Chart
Schedule pipe
This chart cover:
- Schedule 10 Pipe Dimensions
- Schedule 40 Pipe Dimensions
- Schedule 80 Pipe Dimensions
- Schedule 160 Pipe Dimensions
Derived from the formula Schedule=1000×(P/S), where P is pressure and S is allowable stress.
Nominal Pipe Size (NPS): A standardized labeling system for pipe diameters. For example, a “2-inch pipe” refers to its NPS, not its exact dimensions.
Outer Diameter (OD):
Measured in millimeters or inches, OD remains constant for smaller pipes (NPS ≤ 12) but aligns with NPS for larger sizes (NPS ≥ 14).
Wall Thickness:
Determines strength and pressure resistance. For instance, Sch 40 pipe dimensions is thinner than sch 80 pipe thickness, making the latter suitable for high-pressure systems.
Pipe Chart Size – ANSI / ASME
| Pipe Size | OD | ID | Schedules | Wall | Est. LBS per Ft |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/8″ | 0.405 | 0.307 | 10, 10S | 0.049 | 0.1863 |
| 0.269 | 40, STD, 40S | 0.068 | 0.2447 | ||
| 0.215 | 80, XS, 80S | 0.095 | 0.3145 | ||
| 1/4″ | 0.54 | 0.41 | 10, 10S | 0.065 | 0.3297 |
| 0.364 | 40, STD, 40S | 0.088 | 0.4248 | ||
| 0.302 | 80, XS, 80S | 0.119 | 0.5351 | ||
| 3/8″ | 0.675 | 0.545 | 10, 10S | 0.065 | 0.4235 |
| 0.493 | 40, STD, 40S | 0.091 | 0.5676 | ||
| 0.423 | 80, XS, 80S | 0.126 | 0.7388 | ||
| 1/2″ | 0.84 | 0.674 | 10, 10S | 0.083 | 0.671 |
| 0.622 | 40, STD, 40S | 0.109 | 0.851 | ||
| 0.546 | 80, XS, 80S | 0.147 | 1.088 | ||
| 0.466 | 160 | 0.187 | 1.304 | ||
| 0.252 | XX | 0.294 | 1.714 | ||
| 3/4″ | 1.05 | 0.884 | 10, 10S | 0.083 | 0.8572 |
| 0.824 | 40, STD, 40S | 0.113 | 1.131 | ||
| 0.742 | 80, XS, 80S | 0.154 | 1.474 | ||
| 0.614 | 160 | 0.218 | 1.937 | ||
| 0.434 | XX | 0.308 | 2.441 | ||
| 1″ | 1.315 | 1.097 | 10, 10S | 0.109 | 1.404 |
| 1.049 | 40, STD, 40S | 0.133 | 1.679 | ||
| 0.957 | 80, XS, 80S | 0.179 | 2.172 | ||
| 0.815 | 160 | 0.25 | 2.844 | ||
| 0.599 | XX | 0.358 | 3.659 | ||
| 1 1/4″ | 1.66 | 1.442 | 10, 10S | 0.109 | 1.806 |
| 1.38 | 40, STD, 40S | 0.14 | 2.273 | ||
| 1.278 | 80, XS, 80S | 0.191 | 2.997 | ||
| 1.16 | 160 | 0.25 | 3.765 | ||
| 0.896 | XX | 0.382 | 5.214 | ||
| 1 1/2″ | 1.9 | 1.682 | 10, 10S | 0.109 | 2.085 |
| 1.61 | 40, STD, 40S | 0.145 | 2.718 | ||
| 1.5 | 80, XS, 80S | 0.2 | 3.631 | ||
| 1.337 | 160 | 0.281 | 4.859 | ||
| 1.1 | XX | 0.4 | 6.408 | ||
| 2″ | 2.375 | 2.157 | 10, 10S | 0.109 | 2.638 |
| 2.067 | 40, STD, 40S | 0.154 | 3.853 | ||
| 1.939 | 80, XS, 80S | 0.218 | 5.022 | ||
| 1.687 | 160 | 0.344 | 7.462 | ||
| 1.503 | XX | 0.436 | 9.029 | ||
| 2 1/2″ | 2.875 | 2.635 | 10, 10S | 0.12 | 3.531 |
| 2.469 | 40, STD, 40S | 0.203 | 5.793 | ||
| 2.323 | 80, XS, 80S | 0.276 | 7.651 | ||
| 2.125 | 160 | 0.375 | 10.01 | ||
| 1.771 | XX | 0.552 | 13.7 | ||
| 3″ | 3.5 | 3.26 | 10, 10S | 0.12 | 4.332 |
| 3.068 | 40, STD, 40S | 0.216 | 7.576 | ||
| 2.9 | 80, XS, 80S | 0.3 | 10.25 | ||
| 2.624 | 160 | 0.438 | 14.32 | ||
| 2.3 | XX | 0.6 | 18.58 | ||
| 3 1/2″ | 4.000 | 3.760 | 10, 10S | 0.120 | 4.937 |
| 3.548 | 40, STD, 40S | 0.226 | 9.109 | ||
| 3.364 | 80, XS, 80S | 0.318 | 12.51 | ||
| 2.728 | XX | 0.636 | 22.85 | ||
| 4″ | 4.5 | 4.26 | 10, 10S | 0.12 | 5.613 |
| 4.026 | 40, STD, 40S | 0.237 | 10.79 | ||
| 3.826 | 80, XS, 80S | 0.337 | 14.98 | ||
| 3.624 | 120 | 0.438 | 19 | ||
| 3.438 | 160 | 0.531 | 22.51 | ||
| 3.152 | XX | 0.674 | 27.54 | ||
| 4 1/2″ | 5 | 4.506 | STD, 40S | 0.247 | 12.54 |
| 4.29 | XS, 80S | 0.355 | 17.61 | ||
| 5″ | 5.563 | 5.295 | 10, 10S | 0.134 | 7.77 |
| 5.047 | 40, STD, 40S | 0.258 | 14.62 | ||
| 4.813 | 80, XS, 80S | 0.375 | 20.78 | ||
| 4.563 | 120 | 0.5 | 27.04 | ||
| 4.313 | 160 | 0.625 | 32.96 | ||
| 4.063 | XX | 0.75 | 38.55 | ||
| 6″ | 6.625 | 6.357 | 10, 10S | 0.134 | 9.29 |
| 6.065 | 40, STD, 40S | 0.28 | 18.97 | ||
| 5.761 | 80, XS, 80S | 0.432 | 28.57 | ||
| 5.501 | 120 | 0.562 | 35.39 | ||
| 5.189 | 160 | 0.719 | 43.35 | ||
| 4.897 | XX | 0.864 | 53.16 | ||
| 8″ | 8.625 | 8.329 | 10, 10S | 0.148 | 13.40 |
| 8.125 | 20 | 0.250 | 22.36 | ||
| 8.071 | 30 | 0.277 | 24.70 | ||
| 7.981 | 40, STD, 40S | 0.322 | 28.55 | ||
| 7.813 | 60 | 0.406 | 35.64 | ||
| 7.625 | 80, XS, 80S | 0.500 | 43.39 | ||
| 7.439 | 100 | 0.594 | 50.95 | ||
| 7.189 | 120 | 0.719 | 61.71 | ||
| 7.001 | 140 | 0.812 | 67.76 | ||
| 6.813 | 160 | 0.906 | 74.79 | ||
| 6.875 | XX | 0.875 | 72.42 | ||
| 10″ | 10.75 | 10.42 | 10, 10S | 0.165 | 18.65 |
| 10.25 | 20 | 0.250 | 28.04 | ||
| 10.136 | 30 | 0.307 | 34.24 | ||
| 10.02 | 40, STD, 40S | 0.365 | 40.48 | ||
| 9.75 | 60, XS, 80S | 0.500 | 54.74 | ||
| 9.564 | 80 | 0.594 | 64.43 | ||
| 9.314 | 100 | 0.719 | 77.03 | ||
| 9.064 | 120 | 0.844 | 82.29 | ||
| 8.75 | 140, XX | 1.000 | 104.1 | ||
| 8.5 | 160 | 1.125 | 115.6 | ||
| 12″ | 12.75 | 12.39 | 10, 10S | 0.180 | 24.16 |
| 12.25 | 20 | 0.250 | 33.38 | ||
| 12.09 | 30 | 0.330 | 43.77 | ||
| 12.00 | STD, 40S | 0.375 | 49.56 | ||
| 11.938 | 40 | 0.406 | 53.52 | ||
| 11.75 | XS, 80S | 0.500 | 65.42 | ||
| 11.626 | 60 | 0.562 | 73.15 | ||
| 11.376 | 80 | 0.688 | 88.63 | ||
| 11.064 | 100 | 0.844 | 107.9 | ||
| 10.75 | 120, XX | 1.000 | 125.5 | ||
| 10.50 | 140 | 1.125 | 136.7 | ||
| 10.126 | 160 | 1.312 | 150.3 | ||
| 14″ | 14.000 | 13.624 | 10S | 0.188 | 27.73 |
| 13.500 | 10 | 0.250 | 36.71 | ||
| 13.375 | 20 | 0.312 | 45.61 | ||
| 13.250 | 30, STD, 40S | 0.375 | 54.57 | ||
| 13.124 | 40 | 0.438 | 63.44 | ||
| 13.000 | XS, 80S | 0.500 | 72.09 | ||
| 12.814 | 60 | 0.594 | 85.05 | ||
| 12.500 | 80 | 0.750 | 106.1 | ||
| 12.124 | 100 | 0.938 | 130.9 | ||
| 11.814 | 120 | 1.09 | 150.8 | ||
| 11.500 | 140 | 1.250 | 170.2 | ||
| 11.188 | 160 | 1.406 | 189.1 | ||
| 16″ | 16.000 | 15.624 | 10S | 0.188 | 31.75 |
| 15.500 | 10 | 0.250 | 42.05 | ||
| 15.375 | 20 | 0.312 | 52.27 | ||
| 15.250 | 30, STD, 40S | 0.375 | 62.58 | ||
| 15.000 | 40, XS, 80S | 0.500 | 82.77 | ||
| 14.688 | 60 | 0.656 | 107.5 | ||
| 14.314 | 80 | 0.844 | 136.6 | ||
| 13.938 | 100 | 1.031 | 164.8 | ||
| 13.564 | 120 | 1.220 | 192.4 | ||
| 13.124 | 140 | 1.438 | 223.6 | ||
| 12.814 | 160 | 1.594 | 245.3 | ||
| 18″ | 18.000 | 17.624 | 10S | 0.188 | 35.76 |
| 17.500 | 10 | 0.250 | 47.99 | ||
| 17.375 | 20 | 0.312 | 58.94 | ||
| 17.250 | STD, 40S | 0.375 | 70.59 | ||
| 17.124 | 30 | 0.438 | 82.15 | ||
| 17.000 | XS, 80S | 0.500 | 93.45 | ||
| 16.876 | 40 | 0.562 | 104.7 | ||
| 16.500 | 60 | 0.750 | 138.2 | ||
| 16.126 | 80 | 0.938 | 170.9 | ||
| 15.688 | 100 | 1.156 | 208.0 | ||
| 15.250 | 120 | 1.380 | 244.10 | ||
| 14.876 | 140 | 1.562 | 274.20 | ||
| 14.438 | 160 | 1.781 | 308.5 | ||
| 20″ | 20.000 | 19.564 | 10S | 0.218 | 48.05 |
| 19.500 | 10 | 0.250 | 52.73 | ||
| 19.250 | 20, STD, 40S | 0.375 | 78.6 | ||
| 19.000 | 30, XS, 80S | 0.500 | 104.1 | ||
| 18.812 | 40 | 0.594 | 123.1 | ||
| 18.376 | 60 | 0.812 | 155.4 | ||
| 17.938 | 80 | 1.031 | 208.9 | ||
| 17.438 | 100 | 1.281 | 256.1 | ||
| 17.000 | 120 | 1.500 | 296.4 | ||
| 16.500 | 140 | 1.750 | 341.1 | ||
| 16.064 | 160 | 1.969 | 379.2 | ||
| 24″ | 24.000 | 23.500 | 10, 10S | 0.250 | 63.41 |
| 23.250 | 20, STD, 40S | 0.375 | 96.42 | ||
| 23.000 | XS, 80S | 0.500 | 125.5 | ||
| 22.876 | 30 | 0.562 | 140.7 | ||
| 22.626 | 40 | 0.688 | 171.3 | ||
| 22.064 | 60 | 0.969 | 238.4 | ||
| 21.564 | 80 | 1.219 | 296.8 | ||
| 20.938 | 100 | 1.531 | 357.4 | ||
| 20.376 | 120 | 1.812 | 429.4 | ||
| 19.876 | 140 | 2.062 | 483.1 | ||
| 19.314 | 160 | 2.344 | 542.1 | ||
| 30″ | 30.000 | 29.376 | 10, 10S | 0.312 | 98.93 |
| 29.250 | STD, 40S | 0.375 | 118.65 | ||
| 29.000 | 20, XS, 80S | 0.500 | 157.53 | ||
| 28.750 | 30 | 0.625 | 196.06 | ||
| 36″ | 36.000 | 35.376 | 10 | 0.312 | 118.92 |
| 35.250 | STD, 40S | 0.375 | 142.68 | ||
| 35.000 | XS, 80S | 0.500 | 189.57 | ||
| 34.750 | 30 | 0.625 | 235.13 | ||
| 48″ | 48.000 | 47.250 | STD, 40S | 0.375 | 190.74 |
| 47.000 | XS, 80S | 0.500 | 253.65 |
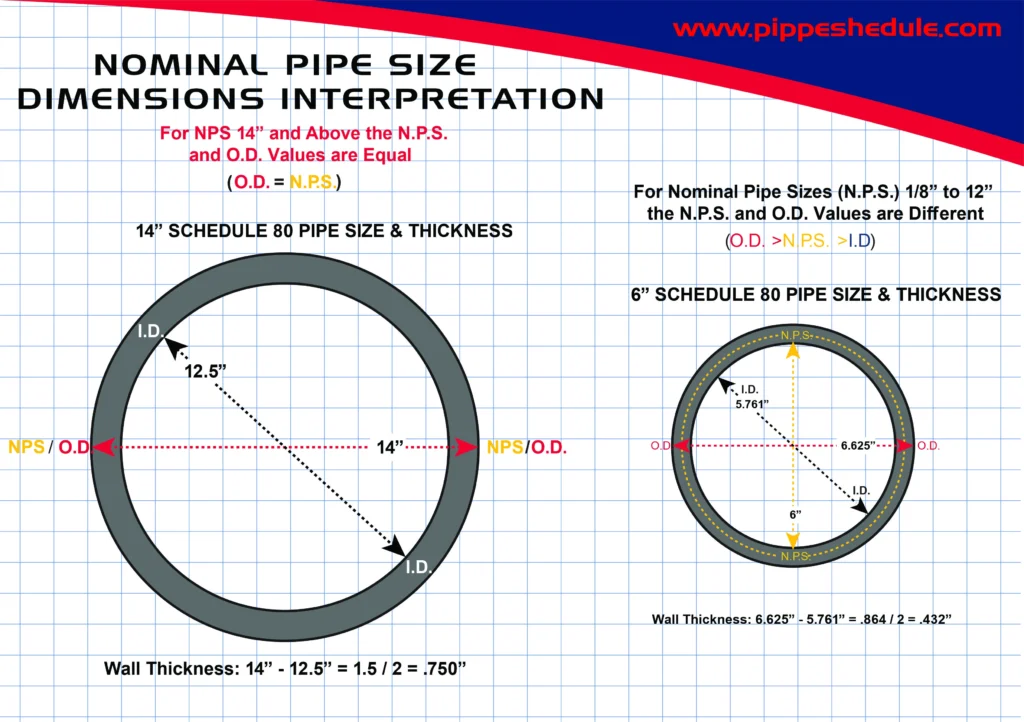
Nominal Pipe Size
This Diagram explain difference in measuring Nominal Pipe Size (N.P.S.) 14″ and Above O.D. Values are Equal (O.D. = N.P.S.)
For Nominal Pipe Size (N.P.S) 1/8″ to 12″ the N.P.S. and O.D. Values are Different (O.D. >N.P.S. >I.D)
Comprehensive Guide to Pipe Schedule Chart
An important tool in the piping, plumbing, and industrial engineering world is the pipe schedule chart. This standardized data is important for professionals who are inclined to select the most appropriate pipes for their application. From calculating pipe wall thickness to working with steel pipes and comprehending nominal pipe size chart (NPS), this guide will provide more light on all you need to know.
What Is a Pipe Schedule Chart?
Tube schedule chart show the relationship between nominal pipe size (NPS), outer diameter (OD), and wall thickness. These pipe schedule chart allow users to identify the essentials like pipe schedule which governs the strength, and durability of the pipe. Standardization in pipe sizes chart ensures uniformity in the industries, hence, making them the most valuable for engineers, architects, and contractors.
Understanding the Piping Schedule Chart
The piping schedule chart categorizes pipes based on their NPS and wall thickness. It is difficult to ensure that the pipe can withstand the required pressure. Below is an example of what a typical pipe size chart includes:
- NPS (Nominal Pipe Size): Defines the approximate diameter of the pipe.
- Outer Diameter (OD): The external measurement of the pipe, often presented in millimeters for global standardization
- Wall Thickness: The thickness of the pipe’s wall, which determines its strength and pressure-handling capacity.
Why Use a Pipe Size Chart?
The pipe size chart makes it easy to refer and select all information at once. Pipe dimension details for steel pipes, wall thickness, and standard pipe sizes in millimeters are included within the compatibility of many systems. Engineers often cross-reference this with the pipe weight calculator to know the load requirements for precise project planning. This would come in handy for oil and gas, construction, and industries in manufacturing.
Schedule 40 VS 80
Steel pipe schedule 40 vs 80 differs mainly in wall thickness and according the pressure rating. Schedule 40 for low-pressure use, while schedule 80 for higher-pressure applications.
Schedule 40 pipe thickness
The thickness varies depending on the pipe’s diameter,
Standard Pipe Sizes in mm
Pipes are categorized not just by NPS but also by their outer diameter and thickness in millimeters. For example:
For a complete piping schedule chart PDF, you can download online resources to keep a handy reference.
Pipe Wall Thickness Chart and Pipe OD Chart in mm
The pipe wall thickness chart complements the pipe OD chart in mm to ensure you clearly understand the specifications for different schedules like Sch 10, Sch 20, and Sch 40. For instance:
- Sch 40 Pipe Thickness: Known for being a balanced choice for strength and cost.
- Sch 80: Offers a thicker wall for high-pressure applications.
Applications of the Steel Pipe Size Chart
Steel pipes are widely used in industries due to their durability and resistance to pressure. The steel pipe size chart ensures:
- Correct fitting for industrial and residential applications.
- Accurate pressure handling for pipelines.
- Consistency in manufacturing and design processes.
Benefits of Using the Nominal Pipe Size Chart
- Ease of Selection: The NPS pipe chart ensures users can quickly identify the right pipe for their project.
- Standardization: Uniform sizing across manufacturers reduces compatibility issues.
- Cost Efficiency: Prevents over-specification, saving on unnecessary material costs.
FAQ
Conclusion
A pipe schedule chart is a crucial tool for selecting the correct pipes based on nominal pipe size, wall thickness, and outer diameter. Whether you’re working on a complex industrial project or a simple home renovation, referencing a sch pipe chart ensures accuracy and reliability. For a detailed guide, consider downloading a piping schedule chart PDF for quick and easy access.
By understanding the basics of pipe size, steel pipe dimensions, and standard pipe sizes in mm, you’ll be better equipped to choose the right materials for your needs.